Table of Contents
Toggle1. Website Design
Website designing is a creative and intellectual task which requires planning and effective execution. The art and science of creating digital environments that smoothly combine utility and aesthetics to produce interesting and user-friendly online experiences is known as website design. It entails the purposeful placement of visual components, including layout, colour scheme, typography, and photography, to effectively draw in customers and communicate the identity of the brand. A well-designed website is more than simply a compilation of pages; it’s a meticulously planned experience that leads users through a smooth information flow and towards the goals they want to achieve. Every element of a website, from the positioning of navigation menus to the choice of call-to-action buttons, is carefully considered from the minute a user lands on it in order to improve usability and promote interaction. The essence of website design is its capacity to arouse feelings, pique visitors’ curiosity, and create a lasting impression even after they have clicked away, regardless of whether the design is sleek and minimalistic or bright and colourful. In the end, website design serves as the link between companies and their audience in the wide world of the internet, influencing opinions, creating bonds, and igniting important exchanges that go well beyond the screen. Let’s understand the process of website design in detail:
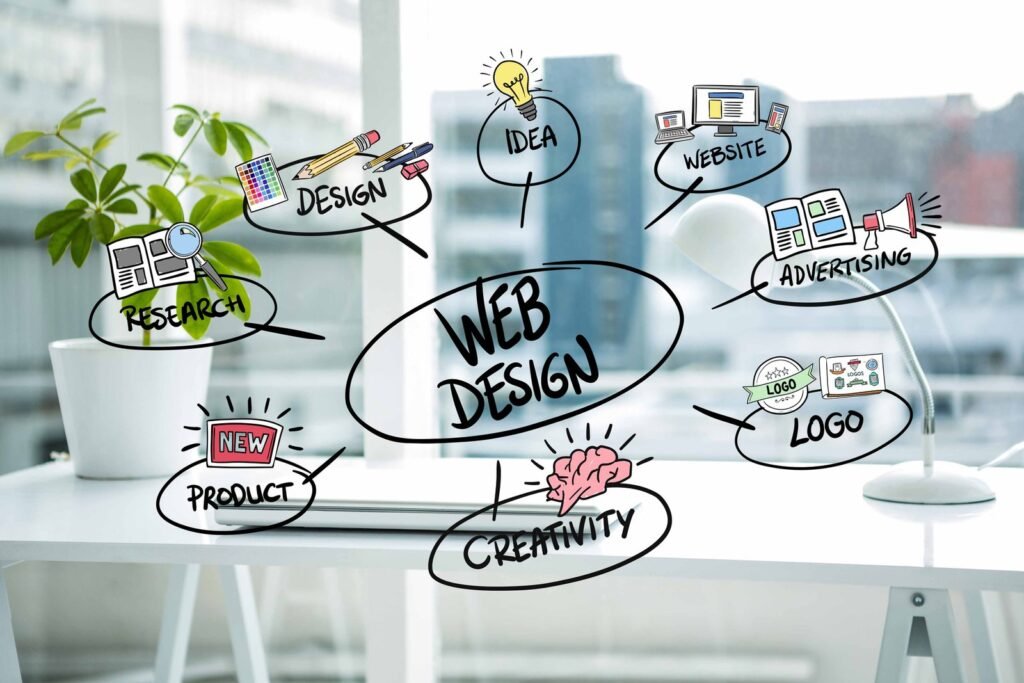
2. Seven main steps in website design
Below mentioned are the seven crucial steps of a website designing process:
Planning and Research: it needs proper planning and research, specify objectives, intended audience, and approach to material.
Design and Development: this phase involves constructing the website, design the visual components, and create wireframes.
Content Creation: it involves composing and compiling text, pictures, and other types of media for the website.
Testing: testing includes verify operation, usability, and browser and device compatibility.
Launch: launch is crucial to make the website live and track its effectiveness.
Maintenance: Update material frequently, address problems, and improve SEO.
Analyse: Monitor performance indicators, solicit input, and make decisions based on information.

3. Goals of Website Design
A website is always conceived and designed with a purpose and an objective, if it is designed with a purpose in head then it will surely serve the purpose for which it is designed. There is a high need to consider the goals of website design in mind while developing a plan for a website. The prominent goals for a website design are:
- To gain wider recognition
- Increasing brand consciousness
- Develop a devoted following
- Build rapport
- Sell goods
- Execute a marketing initiative
- Interaction with users
- Increasing brand consciousness
If a website is designed consciously and purposefully taking all the needs and requirements in consideration, then a website can surely help to attract wider number of people.
4. Prerequisites for website development
Creating a website is now a must in order to gain attention in the online community. All types of businesses, big and small, create websites with the goal of expanding their audience. Website design necessitates the following basic elements:
Domain Name: Your website’s internet address that visitors can reach. Choose a domain name that effectively conveys your brand and is both memorable and pertinent.
hosting websites: Web hosting is a service that manages the files on your website’s storage and online accessible. Use a reliable web host to ensure that your website is always available.
Software: To create and design your website, choose a tool or platform. It’s referred to as website design.
Content: Create interesting and pertinent text, blog entries, product descriptions, and other material for your website in order to draw users in and successfully communicate your message. Create a website that is responsive to several screen sizes and devices so that users on PCs, laptops, tablets, and smartphones can browse it with ease.
SEO Tools: To raise your website’s exposure and position in search engine results, use search engine optimisation (SEO) strategies. Content, meta tags, and URL structures can all be optimised in this way.
Install analytics programmes like Google Analytics to monitor user activity on websites, traffic, and other crucial data that can help you understand how users engage with your website.
5. Various types of website designs
Which website design you will choose will depend on your business requirement and choice. Different audiences, industries, and goals are catered for by the various sorts of website designs available. The following are some typical styles of websites:
Static Websites: These websites, which are usually made with HTML and CSS, have fixed content and layout. Businesses and people who need a basic internet presence with few updates are the greatest candidates for them.
Dynamic Websites: Content on dynamic websites is often updated or modified. Content management systems (CMS), server-side scripting languages like PHP or ASP.NET, and database-driven features are frequently included into them. E-commerce platforms, news websites, and blogs are a few examples.
Single-page websites: These websites offer a simplified and engaging user experience by displaying all material on a single, scrollable page. For landing pages, product launches, and portfolios, they are perfect.
Websites that employ parallax scrolling: When users scroll, background and foreground components move at varying speeds, giving the impression of depth and movement. Websites using parallax effects are visually captivating and are frequently used to tell stories or highlight merchandise.
E-commerce websites: These websites help businesses offer goods and services to customers directly by facilitating online transactions. They have secure checkout procedures, payment gateways, product listings, and shopping carts.
Portfolio Websites: These online displays highlight the talents, accomplishments, and body of work of specific artists or creative professionals. To draw in prospective customers or employers, they usually include galleries, case studies, and contact details.
Blog websites: Blogs are online diaries with regular posts that are chronological in nature and frequently centred around particular subjects or hobbies. They come with features including content organisation categories, archives, and comment areas.
Corporate websites: Acting as a company’s online face, corporate websites include details about their history, goods, services, and contact information. They frequently include components of consumer interaction, marketing, and branding.
Landing pages are independent websites created especially for advertising campaigns, promotions, or lead generation. They are designed with calls-to-action that are enticing enough to turn visitors into leads or customers.
6. Website layouts come in a variety of forms, each with its own components and organisation.
The following are some typical styles of website layouts:
Single Column Layout: Users may easily navigate the website vertically using this layout since all content is displayed in a single column. Simple single column layouts work well for designs that are optimised for mobile devices.
Two-Column Layout: This design separates the content of the webpage into two columns, usually placing sidebars or navigation menus on one side and the main content on the other. In addition to providing a balanced layout, two-column layouts can be used to display navigation options and content at the same time.
Three-Column Layout: This arrangement divides the homepage into three sections similarly to the two-column layout, but it allows more room for additional features or content. Websites with several content categories or intricate navigation systems frequently employ this layout.
Grid Layout: A visually appealing and well-organized design is produced by arranging content into a grid of components that are proportionately or scaled equally. Grid layouts are adaptable and suitable for a range of content kinds, including as text, multimedia, and photos.
Full-Screen Layout: Full-screen layouts give users an immersive and memorable experience by displaying material across the whole browser window. These designs are frequently utilised for websites with visual narrative, landing pages, and portfolios.
Fixed Layout: Regardless of the screen size or resolution, a fixed layout maintains the webpage’s width. Although fixed layouts offer consistency in style, they might not be well-suited to a variety of screens or devices.
Responsive Layout: On desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones, responsive layouts adjust to the user’s device, screen size, and orientation to provide the best possible viewing experience. Flexible grids, media queries, and breakpoints are used by responsive layouts to dynamically modify the layout and design.
Split Screen Layout: This type of layout separates the webpage into two portions, each with contrasting design elements or content. Split screen arrangements are frequently used to highlight features, products, or services and can be quite eye-catching.
One-Page Layout: This type of layout does not require many pages or navigation menus because all content is delivered on a single, scrollable page. Simple landing pages, event websites, and portfolios all benefit from one-page layouts.
These are but a few illustrations of the wide variety of website layouts that are accessible, each with unique advantages and uses. Selecting a layout for your website that works best for your content, goals, and target audience is crucial.
7. Choose Your Website Platform and Design Elements
A website must be both aesthetically pleasing and practical, which requires careful consideration of website platform and design aspects. The following actions will assist you in making wise choices:
Select a Platform for Your Website: When choosing a platform, take your website requirements, budget, and technical proficiency into account. Choices consist of: WordPress is a well-liked content management system (CMS) that has a large plugin ecosystem, versatility, and ease of use.
Wix: A drag-and-drop website builder that’s easy to use and ideal for novices and small enterprises.
Squarespace: A platform that provides integrated tools and expertly crafted templates for e-commerce, portfolio, and blogging websites.
Shopify: An online store-specific e-commerce platform with tools for inventory management, payment processing, and theme customisation.
Determine the Design Components: Choose the functions and graphic components you wish to include in the design of your website. Take into account elements like user experience, target audience, and branding. Important components of the design include:
Logo: Make or upload a logo that stands out on your website and represents your business identity.
Colour Scheme: Pick a colour scheme that complements your brand and expresses the desired tone or style.
Typography: Choose typefaces that accentuate the personality of your business and are easy to read. For emphasis, body text, and headings, use distinct font types.
Imagery: Make effective use of high-quality photos, graphics, and videos to improve visual appeal and convey your message. Create a user-friendly and unambiguous navigation menu to facilitate the swift and effortless retrieval of information by users. Use the “call-to-action” buttons.
Examine Pre-Designed Templates and Themes: If you’re utilising a website builder or content management system, look into pre-designed templates and themes that complement your website’s objectives and style choices. Personalisation and branding are still possible using customisable templates, which can help you save time and effort during the design process.
Think About Mobile Responsiveness: Make sure the platform and design components you choose support responsive design principles so your website can adjust to different screen sizes and devices without breaking a sweat. Having a mobile-friendly website is crucial for both enhancing user experience and search engine rankings.
A visually appealing and easy-to-use website that accomplishes your online goals and successfully conveys your brand message may be created by carefully choosing your website platform and design elements.

8. Crucial Elements of Website Design
A website’s visual design consists of its layout, colour scheme, font, logo, and images. It also captures the overall feel of the website. A brand’s ability to successfully convey its identity and message to customers depends heavily on its visual design.
The focus of user interface (UI) design is on the interactive features of websites, like forms, menus, and buttons that users engage with to navigate and complete tasks. The goal of user interface design is to offer intuitive, user-friendly interfaces that provide smooth interaction and navigation. Optimising the user’s overall online experience is the goal of user experience (UX) design. Information and content organisation are among the factors discussed
Give us a chance to bring a transformation in your work culture by designing website.
Give our Zimo. One professionals a chance to help you create a website that will help your company to reach new heights! Our area of expertise is developing unique websites that increase traffic and engage users. We have the know-how and inventiveness to achieve your goals, 0whether they include raising brand recognition, increasing revenue, or improving web exposure. Working together, we can provide you with a customised strategy that appeals to your target market and fits your company goals. As we collaborate to create a website that distinguishes your company and quickens its growth trajectory, let us be your success partner.


